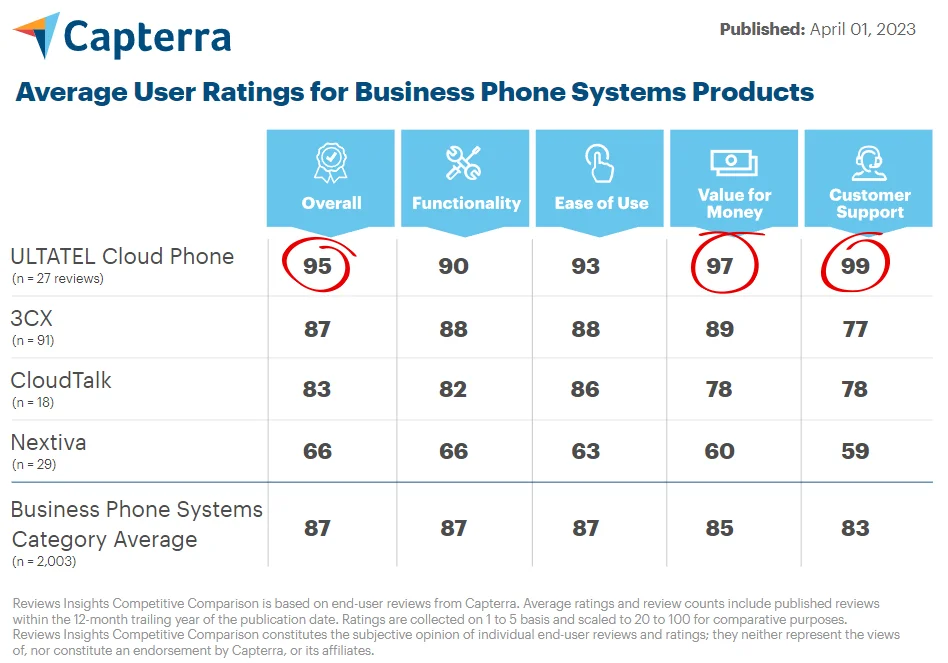
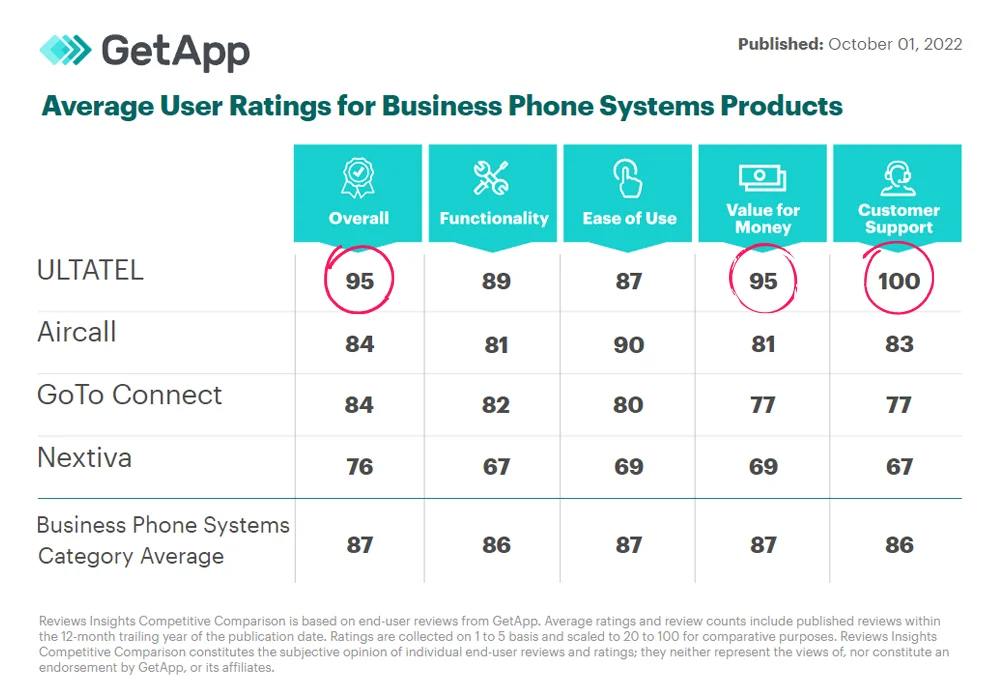
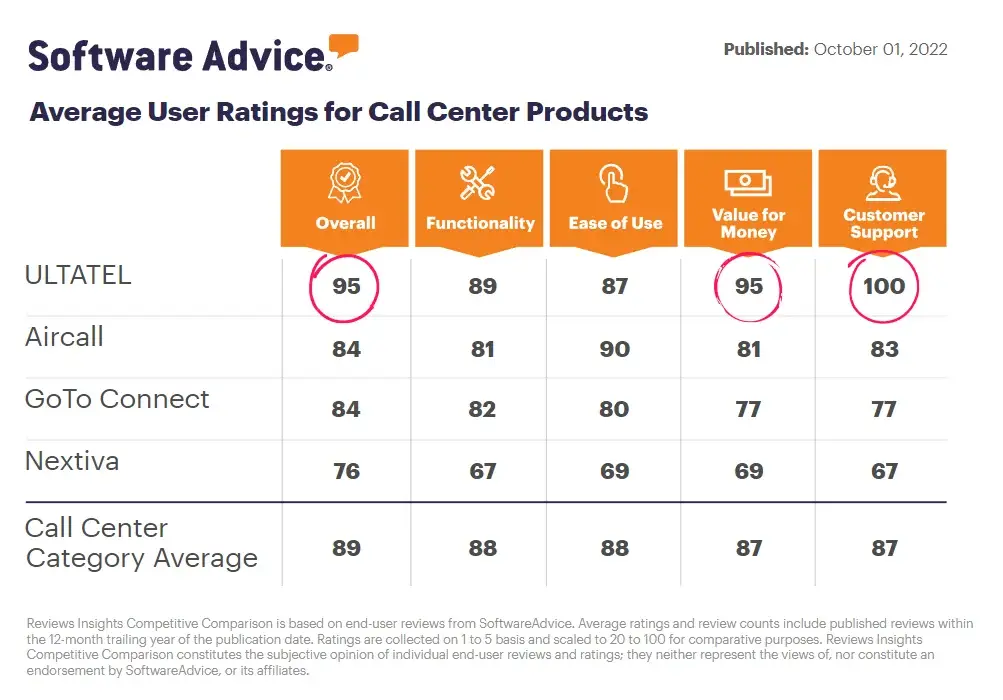
What is a Public Switched Telephone Network?
The Public Switched Telephone Network, or PSTN, is one of the most important and widely used telecommunications systems in use today.
This network uses landline phones and traditional phone lines to facilitate voice communication between different users. It is widely used by call centers, businesses, and organizations that need to handle customer inquiries over the phone.
What Are the Three Major Components of the PSTN??
There are three major components of the PSTN that work together to facilitate voice communication over traditional landline phones.
These include the local exchange, which is responsible for processing calls and routing them to their intended recipient; the long-distance network, which handles calls that need to be routed across different geographic regions; and inter-exchange signaling, which helps coordinate the various components of the PSTN.
How Does the PSTN Work?
The PSTN works by routing calls through interconnected networks that span different geographic regions. When a call is placed, it is first routed to the local exchange, which then uses inter-exchange signaling to connect the call to the long-distance network.
The long-distance network then routes the call to its intended destination, where it is finally connected to the recipient’s phone.
What Are the Benefits of Using the PSTN?
There are many benefits of using the PSTN, including its wide range of coverage, its high level of reliability, and its ability to support a large number of simultaneous calls.
In addition, the PSTN is also easy and inexpensive to use, making it an ideal choice for call centers and businesses that need to handle large numbers of customer inquiries over the phone.