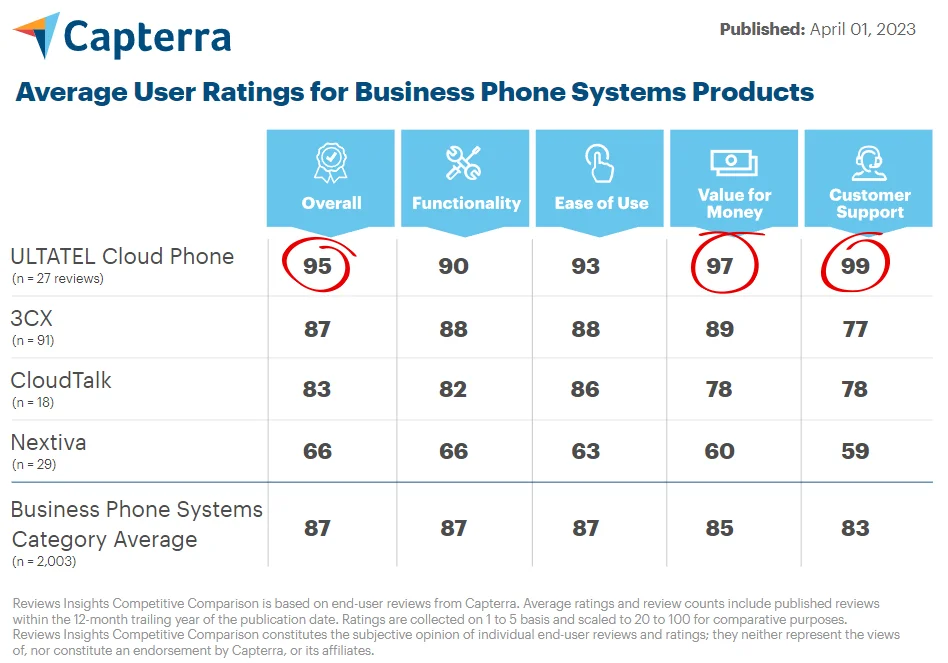
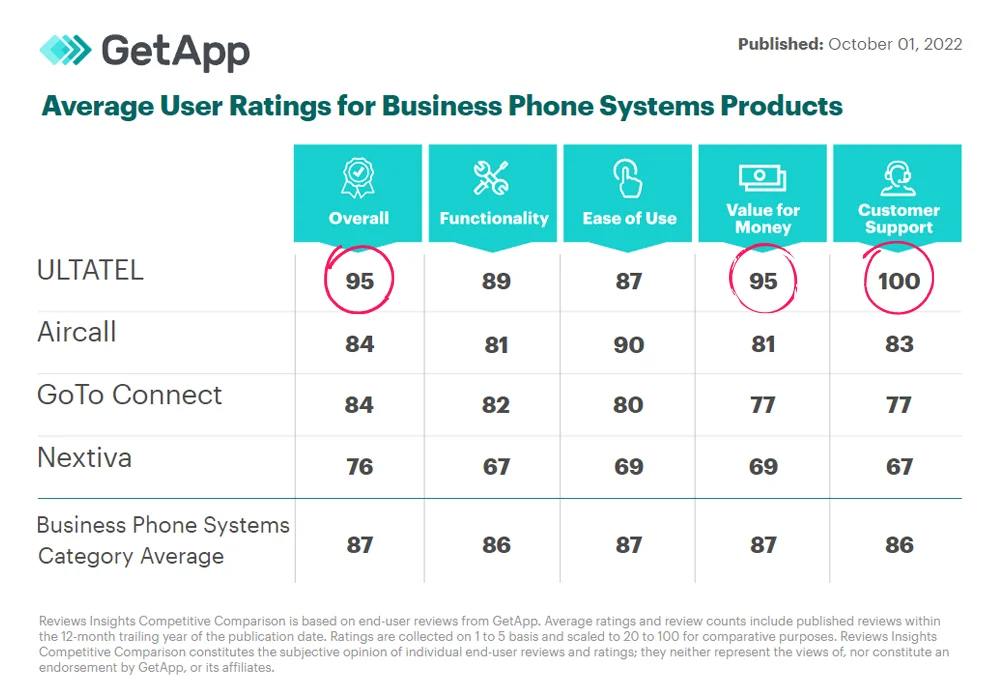
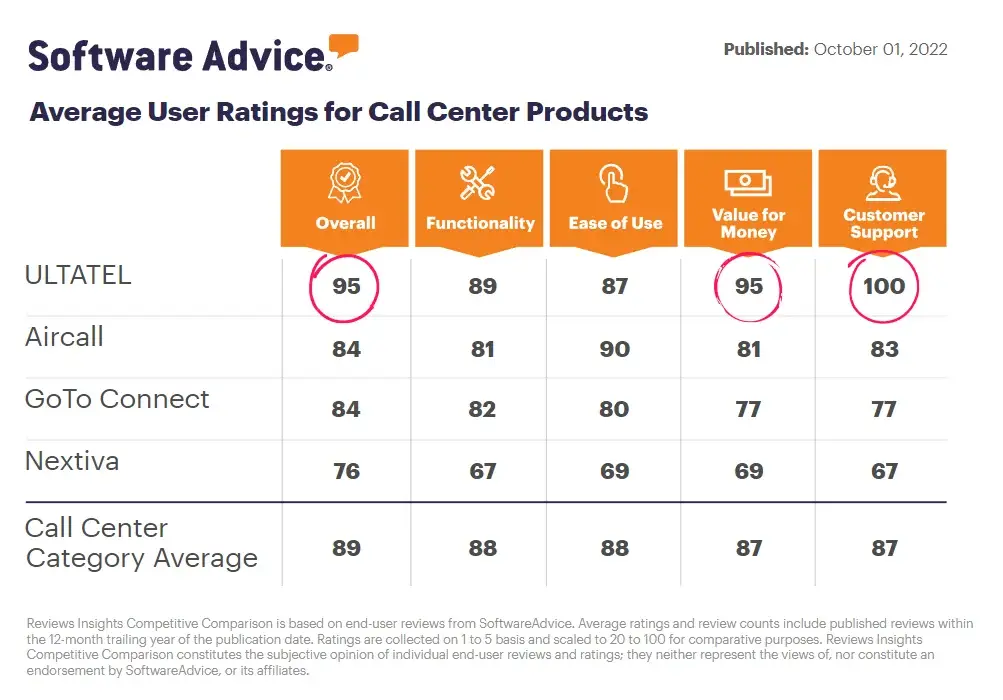
What Is a Data Network?
A data network is a system that allows two or more computers to communicate with each other. The most common type of data network is a Local Area Network (LAN). A LAN connects computers and other devices in a small area, such as a home, office, or school.
A data network can also be a Wide Area Network (WAN). A WAN connects computers and other devices in a large area, such as a city, country, or continent. On top of that – data networks can be wired or wireless. Wired data networks use cables to connect devices. Wireless data networks use radio waves to connect devices.
How Do Data Networks Work?
Data networks make use of different protocols, which send and receive data. The most popular protocol is the Internet Protocol/Transmission Control Protocol (IP/TCP), which is also the protocol used on the internet.
Data is transmitted across a data network in small units called packets. Each packet contains two parts: a payload and a header. The header holds vital information about each packet, such as the source and destination address. And as for the payload, that is the data that is actually being transmitted.
Packets are sent from one device to another over a network path. A network path is made up of a series of interconnected devices, such as routers and switches.
What Are the 4 Types of Data Networks?
There are four different types of data networks. They include:
- A Local Area Network (LAN) is a data network that connects devices within the business.
- A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a data network that connects devices in a large area, such as a city, country, or continent.
- A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), is a data network that is used to connect all of the devices within a metropolitan area – such as that of a city.
- A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a data network that connects storage devices, such as hard drives and tape drives.
What Is the Difference Between a Data Network and a Telephone Network?
A data network is designed to carry digital data. A telephone network is designed to carry analog data. Analog data is a continuous signal, such as the sound of a human voice. Digital data is a series of discrete signals, such as the ones and zeros used in computer data.
Analog data can be converted to digital data, and vice versa. This allows telephone networks and data networks to interconnect and communicate with each other.